3 Describe the Use of Koch's Postulates
Be able to describe the concept of Kochs postulates the scientific method used to determine the infectious cause of disease. Four criteria that were established by Robert Koch to identify the causative agent of a particular disease these include.
Aflatoxin meaning in food.
. Microbiologist Robert Koch Author of Kochs postulates a set of rules for establishing a relationship between a causative microbe and a disease. This means that if a microbe is suspected to be the causative agent of a particular disease it. The suspected etiological agent must be strongly associated with the disease.
The organism must be isolated from an infected host and grown in pure culture in the laboratory. However there are five exceptions to Kochs postulates. The symptom of the disease should be recorded.
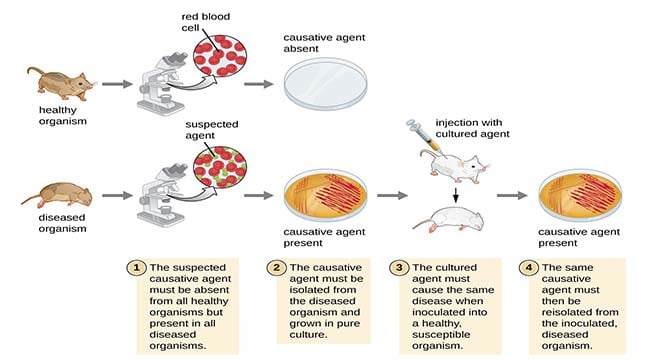
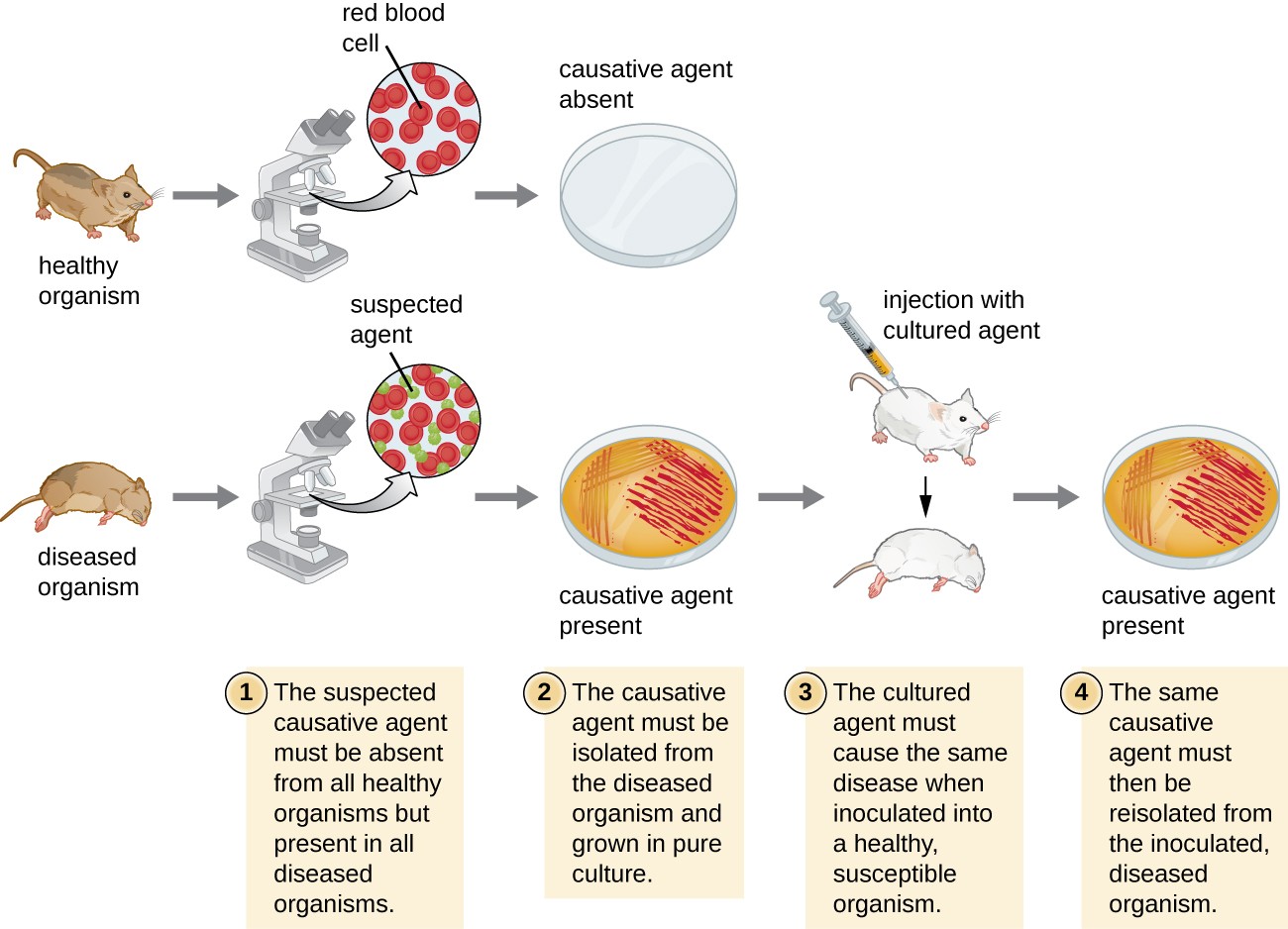
Kochs four postulates are known as Kochs rules or postulates. The postulates are. Diseases caused by different species of microorganisms could elicit similar symptoms.
Kochs Postulates consist of the following four rules. Coli K-12 and E. The pathogens must be found associated with the disease in the diseased plant.
It isnt that they cant see the solution. The microorganism must be found in abundance in all organisms suffering from the disease but should not be found in healthy organisms. Simplified more modern Kochs postulates are the following.
The microorganism can be isolated from the diseased individual and grown in culture. The main tenets of the original Kochs Postulates include 1 recognizing the presence of an agent in all cases of disease 2 isolating that org 3 re-introducing the org causes similar symptoms and 4 the. The postulates were formulated by Robert Koch and Friedrich Loeffler in 1884 based on earlier concepts described by Jakob Henle and refined and published by Koch in 1890.
As originally stated the four criteria are. The microorganism must be identified in all individuals affected by the disease but not in healthy individuals. Collect leaves from their neighborhood or around the school that appear diseased and describe the pathogen signs and symptoms.
3 points Stanley Falkow proposed an updated form of Kochs postulates referred to as molecular Kochs postulates. Kochs postulates were developed in the 19 th century as general guidelines to identify pathogens that could be isolated with the techniques of the day. Which of the Following Is a Composite Number.
The postulates were formulated by Robert Koch and Friedrich Loeffler in 1884 and refined and published by Koch in 1890. We discussed important differences between E. The pathogen from the pure culture must cause the disease when.
The experimental application of Kochs postulates. Even in Kochs time it was recognized that some infectious agents were clearly responsible for disease even though they did not fulfill all of the postulates. These are described in.
The pathogen must be isolated from the diseased host and grown in pure culture. Changing how we think about infectious diseases. How Long Are Brats Good for After Sell by Date.
Kochs postulates are a series of ground rules to. Transfer of the suspected pathogen to an. The pathogen should be isolated grown in pure culture in artificial media.
The microorganism must be isolated from a diseased organism and. Developed in the 19 th century Robert Kochs postulates are the four criteria designed to assess whether a microorganism causes a disease. When the organism from the pure culture is inoculated into a susceptible host.
The pathogen from the pure culture must cause the disease when it is inoculated into a. Kochs belief that only one pathogens causes one disease has now been called into question as multiple postulates are increasingly considered out of date. The bacteria must be isolated from the host with the disease and grown in pure culture.
Describe how a researcher could use molecular Kochs postulates to explain the pathogenicity of E. If all such steps are followed and proved true then the isolated pathogen is identified as the organisms responsible for the disease. The pathogen can be isolated from the diseased host and grown in pure culture.
The suspected pathogen can be isolated - and propagated - outside the host 3. These postulates really served as the foundation for medical microbiology and offered a systematic approach to the study of microbes that cause disease. Kochs postulates are mostly possible with pathogens like bacteria fungi parasitic higher plants nematodes and some viruses.
Sets with similar terms. Some microorganisms could not be cultured in artificial media. What they are and what they explain 1.
Isolate and identify a plant pathogen from fruit inoculate. Some pathogens can cause several disease conditions. Kochs Postulates The Evolution of Kochs Postulates.
May 3 2018. The microorganism or other pathogen must be present in all cases of the disease. Today are known as Kochs Postulates.
Kochs postulates are the criteria that establish a causative relationship between a microbe and a disease. A specific organism must always be observed in association with the disease. Words That Start With U That Describe Someone.
Kochs postulates were invaluable at the time they were developed and remain largely. The same pathogen must be present in every case of the disease. 3 Inoculation of a healthy individual with the.
Kochs postulates are as follows. The bacteria must be present in every case of the disease. The cultural characteristics of the pathogen should be noted.
Acson Car Air Purifier. Kochs postulates vs molecular Kochs postulates. How Many Inches Are There in 12 Feet.
Describe Word for Someone Who Likes to Help Others. Which of the Following Is a Carboxyl Group. 3 Describe the Use of Kochs Postulates.
The specific disease must be reproduced when a pure culture of the bacteria is inoculated into a healthy susceptible. Was born in 1843. Kochs postulates are four criteria designed to establish a causative relationship between a microbe and a disease.
Koch applied the postulates to describe the etiology of cholera and tuberculosis both of. In part 3 of this series we were introduced to Kochs experimental requirements Postulates. 2 The microorganism must be cultured from the diseased individual.
This article describes those exceptions to Kochs postulates in. 1 The microorganism must be found in diseased but not healthy individuals.


0 Response to "3 Describe the Use of Koch's Postulates"
Post a Comment